Organization of Local Government
One of the most frequent asked by foreigners is what type of government we have. Trinidad and Tobago has a parliamentary democracy, which was inherited from Britain after gaining independence on August 31st, 1962. Trinidad and Tobago became a Republic state in 1976, which means that the country is "owned" by all citizens (as compared to a monarchy), and is governed by representatives elected by the public.
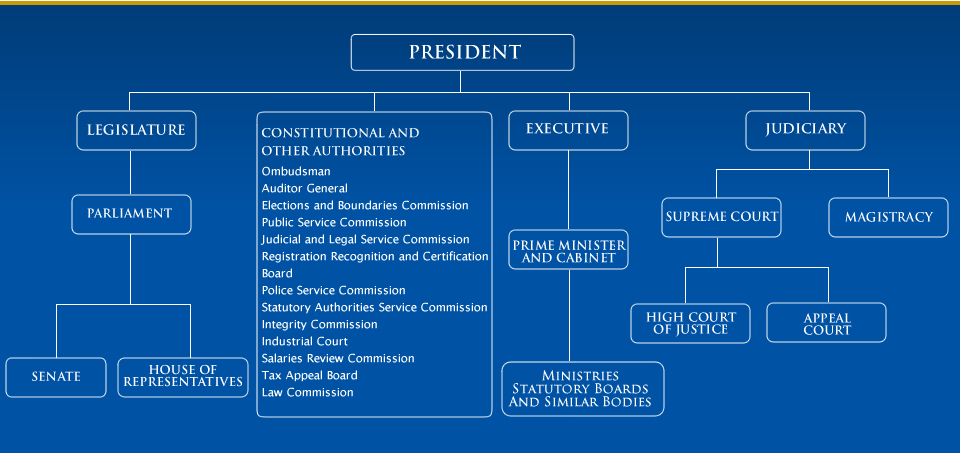
The President is the Head of State and is the nominal source of executive power, meaning that they do not have an active role in parliament but must still assent to all bills passed in both Houses of Parliament before they become law. The president is elected by all members of the Senate and the House of Representatives, and serves a five year term.
There are three branches of government:
Executive Branch
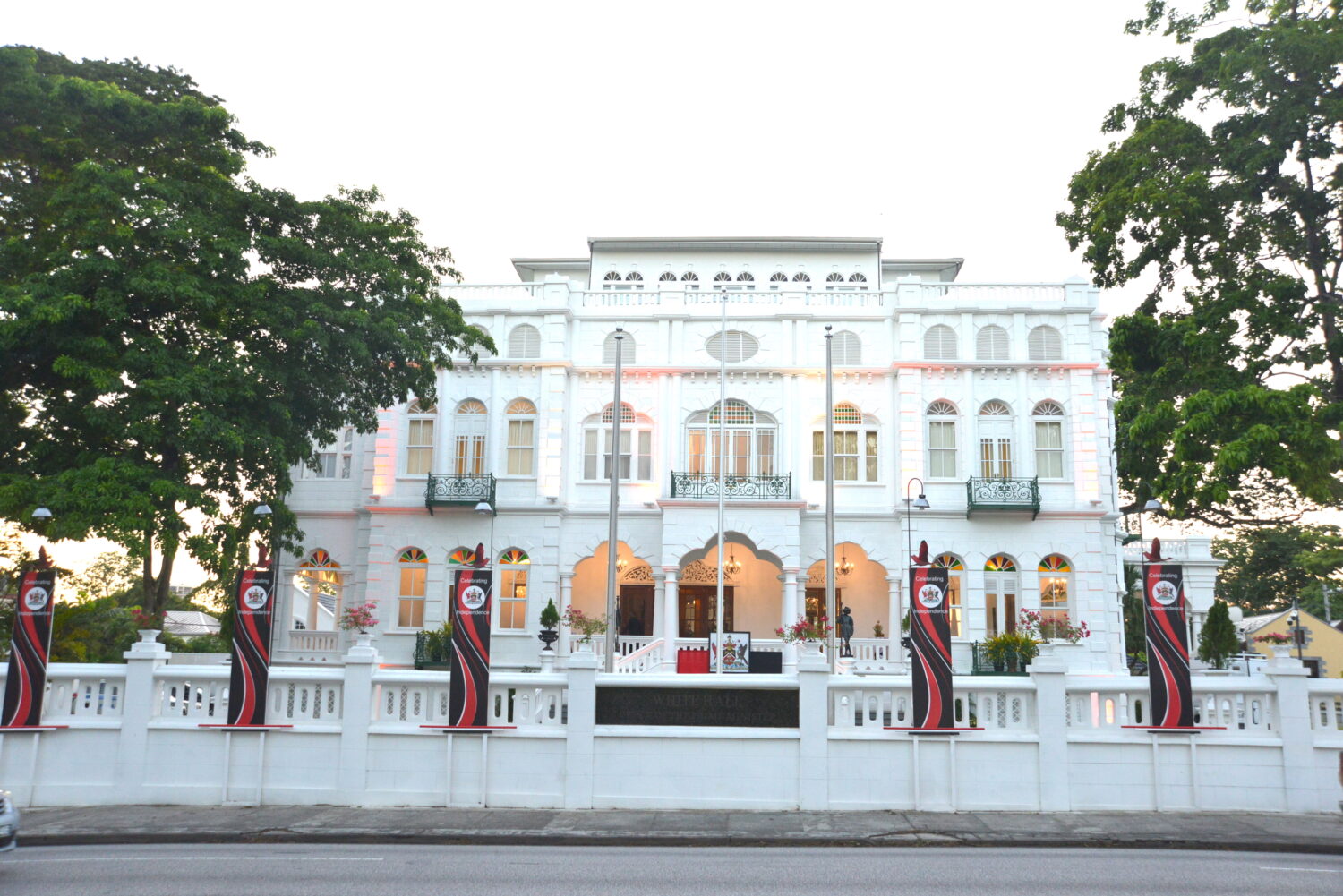

Whitehall is the official office of the Prime Minister
The Executive Branch is comprised of the Prime Minister and the Cabinet. The Cabinet refers to the Ministers for each government Ministry (Ministry of Finance, National Security, Housing and Urban Development, Public Utilities, Education, etc.), which is led by the Prime Minister. The Prime Minister is appointed by the President as the person with the most support from the House of Reprsentatives, which is usually the leader of the poiltical party that won the election. The Cabinet effectively has control of the nation's affairs through the different Ministries.
Click here for a list of the different Ministers and the current Ministers.
Legislative Branch
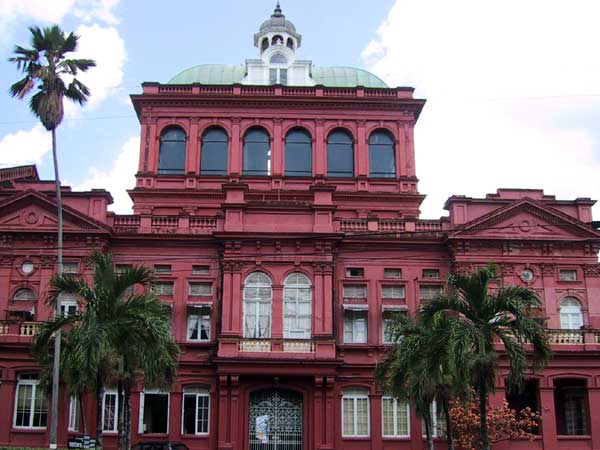

Parliament is located in the Red House
The Legislative branch of government, more commonly referred to as Parliament is responsible for debating and passing laws for the peace, order and good governance of Trinidad and Tobago. It is comprised of the Senate and the House of Representatives.
The Senate has 31 members appointed by the President based on the advice of the Prime Minister, the leader of the Opposition, and to represent the sectors of civil society. The House of Representatives has 41 members, who are elected by the public in the general elections to represent their constituencies. Click here for a list of the constituencies.
Tobago has its own elected House of Assembly responsible for the administration of the island, and for the implementation of policies that are referred by Parliament.
Judicial Branch
The third branch of government is the Judiciary, which is responsible for administering justice. The Court of Appeal is the country's highest court, and is headed by the Chief Justice The Chief Justice is appointed by the President on advice of the Prime Minister and the leader of the Opposition.
Discussion Questions
Here are some questions that can help you understand this topic better:
- What type of government do we have?
- What are the differences between the roles of the President and the Prime Minister?
- Describe the three branches of government and their function
- What government officials can you name along with their post?
- What constituency do you live in and who is the elected member in the House of Representatives?
